– Optimal sensing circuit for magneto-impedance element vastly enhances power efficiency –
Researchers) AKITA Ippei, Senior Researcher, Advanced Integrated Circuit Research Group, Device Technology Research Institute
- Development of a magnetic sensor using a low power consumption integrated circuit for measurement and a magneto-impedance element
- Sensor energy efficiency enhanced by 1000 times and noise reduced to 1/100
- Expected to contribute to compact, high-sensitivity, and lower power consumption sensing for applications such as biomagnetic measurement and industrial application measurement
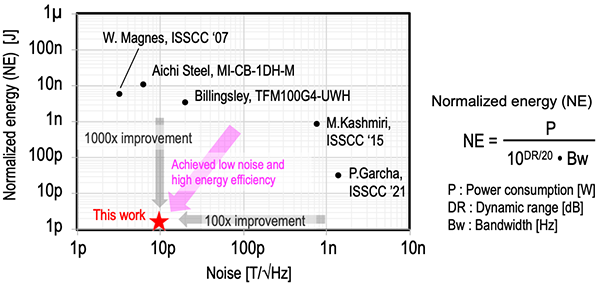
Comparison of performance of developed magnetic sensor
Low-noise, wideband magnetic sensors are required in a wide range of fields such as biomagnetism including magnetoencephalography and magnetomyography, automated driving, nondestructive inspections, and current sensing. However, in order to avoid signal saturation due to fluctuations in the environmental magnetic field, a high dynamic range and low power consumption operation are also demanded. Furthermore, applications such as implantable biomagnetic measurement require a scale on the order of several mm due to implantation space constraints, and smaller and lighter magnetic sensors are also demanded for other applications.
Chip-sized magnetic sensors that use an integrated fluxgate type have been developed as compact and wideband magnetic sensors, but these have high magnetic noise at the nanotesla (nT) level. On the other hand, magnetic sensors with low noise approaching the picotesla (pT) level tend to have a larger size and drive current, which is disadvantageous for compact mounting. Thus, it is a challenge to simultaneously achieve low noise, low power consumption, and miniaturization for applications such as biomagnetic measurement.
In collaboration with Aichi Steel Corporation, researchers in AIST developed an application-specific integrated circuit (hereafter “ASIC”) for a low-noise, wideband magnetic sensor base on a magneto-impedance element (hereafter “MI element”) developed by Aichi Steel Corporation
This ASIC has a new signal processing circuit capable of low power consumption operation, and appropriately amplifies the voltage signal that changes in response to the external magnetic field obtained from the MI element. In addition, low noise and wideband characteristics are achieved by a digital auto-correction circuit that maximizes the sensing sensitivity of the MI element. Furthermore, normalized energy, which is a metric calculated by power consumption and magnetic field detection performance, is improved by 1000 times compared to conventional fluxgate type magnetic sensors, and noise is reduced to 1/100 compared to integrated fluxgate type magnetic sensors. Use of the developed magnetic sensor is expected to realize a compact sensing system with high sensitivity and low power consumption for applications such as biomagnetic measurement and industrial application measurement.