At AIST (Hiroyuki Yoshikawa, President), the Diamond Research Center (Naoji Fujimori, Director), and the Diamond Wafer Team (Yuji Horino, former Team Leader; Akiyoshi Chayahara, current Team Leader; Yoshiaki Mokuno, Senior Research Scientist), in collaboration with Sato Yakuhin Kogyo Co., Ltd., Kurita Seisakusho Co., Ltd. (Yoshio Kurita, CEO), and the Nara Prefectural Institute of Industrial Technology (Shinsuke Yamanaka, Director; Yasuhiro Miki, General Researcher; Shigehiro Adachi, Senior Researcher; Tadashi Taniguchi, General Senior Researcher) have succeeded in developing a new type of precision die (pestle) for pharmaceutical tableting that lasts at least 3.5 times longer than conventional hard chromium plated and chromium nitride dies.
The present results were obtained from a process using the plasma-based ion implantation & deposition system (PBII&D) developed jointly by AIST and Kurita Seisakusho Co., Ltd. to adhere a DLC film (DLC) to the surface of metallic dies at the Nara Prefectural Institute of Industrial Technology, where they were subjected to long-term continuous tableting tests. After the prototype dies (pestles) coated with DLC were subjected to more than 336,000 strikings, no surface damage was found, and there was no decrease in tablet hardness. Moreover, there were almost no problems such as sticking and capping that are encountered during conventional tableting. The new dies have a very long useable life, and their cost is only about 1.5 times higher than conventional dies.
 |
|
Figure 1 The prototype precision die (pestle) for tableting: Size of edge diameter φ = 8 mm
|
Contract processing companies play an important role in the medical and pharmaceutical industries of Japan. This is especially true in Nara Prefecture, where contract drug processors can lead the way to new fields such as product production in close connection with major pharmaceutical companies. In addition, with the revision of the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law, contract drug processors will become even more active in consignment production.
Against this backdrop, abrasion and other damage to precision dies (pestles) for making tablets are becoming a major problem. At the same time, from safety, environmental, and recycling perspectives, there is great demand for making high-precision, high-performance, long-life dies for tableting by using new film-coating technology instead of the current dies made with hard chromium plating, chromium nitrides, etc.
In FY 2004, AIST and Kurita Seisakusho Co., Ltd. began joint research on the production of high precision dies (pestles) for tableting that would use film-forming technology from the plasma-based ion implantation & deposition system. AIST contracted part of this research to the Nara Prefectural Institute of Industrial Technology in an effort to enhance the adhesion between the steel base materials and the DLC film. To apply the results of this research to the high-precision dies (pestles) for tableting, in FY 2005, with assistance from Sato Yakuhin Kogyo Co., Ltd., long-term continuous tableting tests were begun using magnesium oxide powder at the Nara Prefectural Institute of Industrial Technology as a model tablet material. On-going tests have been conducted on its durability.
It should be noted that this joint research was supported by the FY 2004 (Joint) Research & Development system for supporting regional small and medium enterprise.
1) Preparation of the DLC film, surface processing, and film characteristics
To produce the DLC film, an original substrate processing method was applied to the surfaces of the alloy tool steel (JIS G4404: SKD11) and the high-speed tool steel (JIS G4403: SKH51), then the substrates of these materials were given a coating of DLC film using film-coating technology from the plasma-based ion implantation & deposition system.
2) Application of DLC film to the high-precision dies (pestles) for tableting
DLC film was formed on the surface of the precision dies (pestles) for tableting, then an investigation was conducted to determine the relation between striking pressure and tablet hardness during the initial filling stage using magnesium oxide powder as a model tablet material. With assistance from Sato Yakuhin Kogyo Co., Ltd., high-pressure tableting tests were conducted at the Nara Prefectural Institute of Industrial Technology. As a result, the pestles coated with DLC film showed almost no abrasion and almost no lamination of the film, and far surpassed the useable life of conventional hard chromium-plated dies (pestles).
3) Evaluation of the durability and utility of the DLC film based on the long-term continuous tableting test
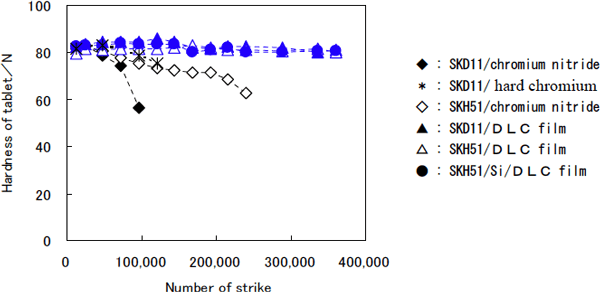
Long-term continuous tableting tests were conducted under conditions of striking pressure of 18-19 kN and striking speed of 40/min to evaluate the durability and utility of the die. In the case of conventional pestles plated with chromium or coated with chromium nitride, the coating peeled off after about 96,000 strikes, and the corners of the pestles showed significant wear and abrasion. There was also sudden occurrence of sticking phenomenon, and tablet hardness rapidly decreased. However, in the case of pestles coated with the newly developed DLC film, there was almost no damage of the pestle surface and almost no decrease in tablet hardness, even after more than 336,000 strikes. Moreover, with the new film there was almost no tableting-related problems like sticking or capping, proving that the durability of the new dies (pestles) was at least 3.5 times greater than that of dies coated with chromium nitride (see Figs. 2 and 3)
 |
|
Figure 2 Changes in tablet hardness during the continuous tableting test
|
 |
|
Left: Conventional product, SKH51/chromium nitride film
|
|
Right: Newly developed SKH51/DLC film
|
|
Figure 3 State of the pestle surface after the continuous tableting test
|
The results from this research should be able to provide consistent quality control in pharmaceutical processing and make a significant contribution to cost reduction in tablet manufacturing. Moreover, plans call for the precision dies (pestles) for tableting developed here to be sold by Kurita Seisakusho Co., Ltd. This new technology appears to be suited not only for the pharmaceutical industry, but also for the food industry and other processing industries that use the same types of molding dies, and work will begin on developing new applications.