Development of a Catalyst Capable of Synthesizing Methanolfrom Carbon Dioxide at Room Temperature
- HIMEDA Yuichiro, ONISHI Naoya
Global Zero Emission Research Center
- KANEGA Ryoichi
Research Institute for Energy Conservation
Released: January 14, 2021
A catalyst capable of synthesizing methanol from carbon dioxide at low temperature and pressure
A multinuclear catalyst with two iridium centers precisely arranged in the catalyst was developed, and methanol was successfully synthesized from carbon dioxide and hydrogen under low temperature and pressure conditions.
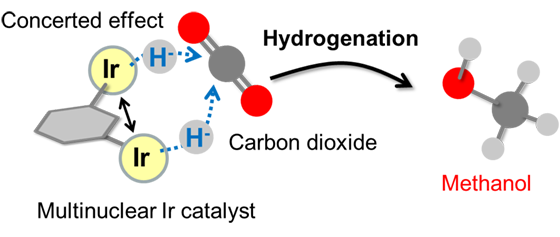 |
| Methanol synthesis by hydrogenation of carbon dioxide using a multinuclear iridium catalyst |
More efficient production of methanol from carbon dioxide
Intensive efforts are underway to develop catalysts for producing methanol, as a raw material such as plastics and fuels, from carbon dioxide. Conventional solid catalysts require high temperatures (>200°C), so many problems for practical application remain, such as low conversion by thermodynamic equilibrium restriction and low selectivity.
Synthesis of methanol from carbon dioxide at low temperature and pressure
When the newly developed multinuclear iridium complex catalyst is reacted in the solid state with a mixed gas of hydrogen and carbon dioxide, the carbon dioxide is successfully converted to methanol even at 30°C or 0.5 MPa. Furthermore, no methane or carbon monoxide was detected. This is thought to be due to the concerted reduction of carbon dioxide by two highly active iridium centers precisely arranged in the catalyst. The generated methanol exists in gas phase, so it is easily recovered and can be applied to flow processes.
Leading to catalyst processes for realization of carbon recycling technology
The researchers aim to further improve catalyst performance and reduce costs. Efforts will also be made to develop flow processes and practical processes in order to further improve methanol productivity from CO2.
Contact for inquiries related to this theme
Global Zero Emission Research Center
HIMEDA Yuichiro, Prime Senior Researcher
AIST Tsukuba West, 16-1 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8569 Japan
E-mail: gzr-info-ml*aist.go.jp (Please convert "*" to "@".)
Research Institute for Energy Conversion
KANEGA Ryoichi, Researcher
AIST Tsukuba Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8565 Japan
E-mail: M-ene-storage_all-ml *aist.go.jp (Please convert "*" to "@".)