Point
We have developed a technology for integrating ultrathin sensors and circuit chips on a flexible board using MEMS technology, and fabricated a flexible 2D-strain-pattern sensor. We have also stuck the sensor on a highway bridge to monitor the dynamic strain distribution of the bridge caused by the passage of vehicles.
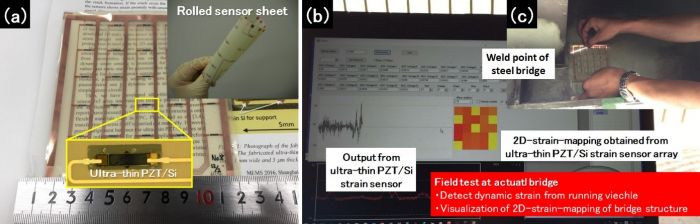
(a) Overall and enlarged views of developed sensor, (b) and (c) Situation of strain distribution measurement near steel bridge welding part using sensor
|
Background
In recent years, contrary to an increase in the number of old bridges, skilled specialized workers have been short in number, and inspection and progress observations have been delayed. Strain distribution measurement using strain sensors is promising, but has the problems of high cost and poor workability. AIST is developing various monitoring systems using wireless MEMS sensors, such as ones for landslide disaster, infrastructure, and vital signs. In collaboration with Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd. (DNP) who has a functional film business, we have worked on developing a bridge strain distribution sensor having durability in outdoor environments and a high workability.
Outcomes and Methods
By combining AIST’s mounting technology for ultrathin flexible boards and DNP’s technology for integrating a protective film and an adhesive film, we have developed a wirelessly communicable flexible 2D-strain-pattern sensor capable of being easily stuck on site. When a vehicle runs over a bridge, the sensor is strained together with the bridge, thus making it possible to measure dynamic strain distribution with high sensitivity.
Future Plan
We will stick the sensor on a highway bridge to perform strain distribution measurement and outdoor durability evaluation, as well as perform a verification test on progress observation of a repaired and reinforced bridge. We will also examine cost reduction by using a large board.
Contact
 |
|
Takeshi Kobayashi
Leader
Socially-Integrated Sensor System Research Team, Research Center for Ubiquitous MEMS and Micro Engineering
AIST Tsukuba East, 1-2-1 Namiki, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8564, Japan
TEL: +81-29-861-7100
FAX: +81-29-861-7225
E-mail: umemsme_web-ml*aist.go.jp (Please convert “*” to “@”)
|