– Practical glass with high light and heat resistance that can be shaped by users –
Researchers: Hirokazu Masai, Senior Researcher, Advanced Glass Group, Inorganic Functional Materials Research Institute
Using a liquid-phase reaction, the researcher has developed transparent, colorless, low-melting glass that melts at temperatures as low as 500 °C, and has enhanced its water resistance by improving the glass composition. He has demonstrated that the glass has higher light and heat resistance than polycarbonate (PC).
 |
|
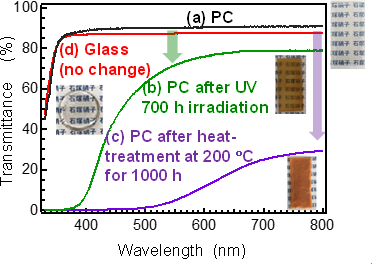
Figure: Comparison between the developed glass and PC |
Ordinary glass has high heat and light resistance and high optical transparency, but needs to be heated to 800 °C or higher for melting and shaping. Although sol-gel method is a method to fabricate glass at lower temperatures, this method requires rebaking at about 1000 °C for densification. A process technology was needed that allows the glass fabricating process, from liquid-phase synthesis to shaping, to be performed in a low-temperature range close to that for plastic.
The developed glass does not contain organic compounds but softens at a low temperature (glass transition temperature: approximately 235 °C), enabling shaping at low temperatures. The glass contains phosphate unit as a main component but has a practical level of water resistance due to improved glass composition. The researcher conducted accelerated light and heat resistance tests. The optical transparency of the developed glass remained constant, while that of PC showed a significant decrease. LED applications of the developed glass are expected.
For practical application of the developed low-melting glass, the researchers will optimize the reaction process based on an analysis of the glass structure and design materials for specific purposes.