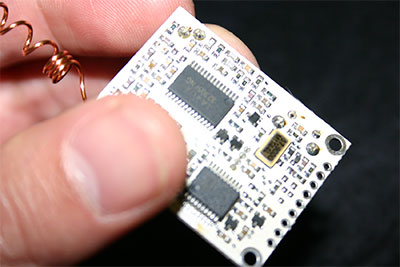
The Intelligent Systems Institute (ISI) of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), an independent administrative institution, has developed an ultra- slim network node of battery-powered wireless type in collaboration with Ymatic Co., Ltd. (Ymatic hereinafter). See Photo. 1. The node is able to identify up to ten million nodes physically, and expected to accelerate extensively the realization of ubiquitous community, as well as, the application to active IC tags for logistics and information management.
 |
|
Photo 1. Newly developed ultra-slim network node |
The ISI-AIST has previously proposed a concept of "ubiquitous function" to efficiently use every appliance and device distributed in household and office spaces anticipating the materialization ubiquitous robot community in near future. As a part of this technology, efforts have been paid to the development of new communications terminal of higher degree of freedom and I/O features to replace existing information outlets on IC tags.
The newly developed network node will make it possible to implement wireless connection with every electrical appliance and sensor in home and office, as well as household robot to be available in future, and is expected to contribute to the realization of ubiquitous community friendly to aged people.
The newly developed network node is of extreme energy saving design theoretically ensuring 60-year or longer continued operation with a single button-type battery. Owing to long service life without battery replacement, the node may be installed in a building at the time of construction. Moreover, as the node is of size and weight comparable to or smaller than a remote control device for keyless entry to an automobile, and estimated to be priced as low as an ordinary USB connection cord, it may be used as a new active type IC tag in the world of logistics.
The conventional IC tags are of passive type without I/O capability with outside devices nor internal information processing. The newly developed node is equipped with internal info-processing and wireless communication capability, and can identify the distribution steps, opening the way to an innovative deployment in the logistic world.
In the development of the ultra-slim network node, realizing the ubiquitous function concept of the ISI-AIST, Ymatic, one of venture enterprises authorized by the AIST has participated in design and instrumentation.
The result will be reported at a Meeting of System Integration Division of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers (SI2004, SICE) to be held at Tsukuba, Ibaraki, December 17 through 19, 2004.
The IC tag is a semiconductor device consisting of an IC chip to store information and an antenna for wireless communication. In contrast to the bar code, the IC tag with data communication capability is expected to innovate the logistic world by reading data from tags posted at a hidden place. For instance, tagging every article in a supermarket clears off accounting by simply passing a basket filled with picked goods through a checkout counter. Demonstration trials of instantaneous accounting with an unattended counter have been made globally.
On the other hand, in the robotic study, it has been attempted to make a space functional by embedding element devices of robotic system in the relevant environment. With the conventional element devices, the system configuration is based on wired connection, complicating the system construction and hampering the practical application and operation.
The ISI-AIST has been studying the robot control system embedded in the environment based on a concept that individual robotic elements are not always to be concentrated at a particular site owing to the development of wireless and network communications. (AIST Press Release, November 11, 2003: "Development of Distributed Knowledge Robot Control System Using IC Tags".)
In the R&D process, it is necessary to install some efficient means of sensing and communication functions in wall, ceiling and general 3D environment, and new terminals are to be developed to replace IC tags equipped with no I/O features.
General purpose terminals developed for an element module of the sensor network may be represented by Nest/Smart Dust under R&D by an international open forum headed by the University of California, Berkeley. However, as the baud rate and microcomputer spec for this module far exceed the actually needed performance, the price will be so high that the device seems to be not applicable to the environment-installed system.
The newly developed network node has baud rate and microcomputer specifications held moderate in consideration of actual application scene, and at the same time, has been designed for slim size and reduced energy consumption through the development of energy saving algorithm.
The main feature of the node includes digital I/O function, 8-bit microcomputer and system configuration capable of accepting various software requirements. With the microcomputer and the communication device set in standby mode by software, and activated once in 5 seconds, the system can be driven with a single button battery for a year or longer. The power consumption of the new node is 1/10 that of ZigBee driven by two alkali AA batteries for two years. The size is about 6.0 cm3, the smallest among battery-powered terminals in the world. Using 300 MHz wireless of very weak output, requiring no license, the node is provided with 24-bit terminal ID and dozen-meter coverage.
The newly developed network node is characterized by highly versatile specifications, allowing application as long reading range IC tags by adding sensor and actuator modules. For instance, the node may be used for automatic door of high security. For this reason, the node is readily applied to the sensor network, and the present achievement will accelerate the implementation of a sensor network system.
 |
|
Major Specification for Newly Developed Ultra-Slim Network Node |
-
Terminal for sensor network with world-smallest size: volume 6.0 cm3 (2.8 cm x 3.6 cm x 0.6 cm, with antenna excluded)
-
Very weak wireless output at 300 MHz, no license required
-
Dozen-meter coverage in sight distance
-
Provided with 7-color LED and switch
-
Continued operation (in a mode of an access in every 5 seconds) for longer than a year with a button battery. In a mode of an access in every 5 minutes, for 60 years theoretically.
-
A microcomputer and a two-way communication module included
-
Digital I/O function for sensor
-
Adaptable to ZigBee with software altered
-
24-bit terminal ID up to 16,777,216 items
-
To be marketed from Ymatic
-
lSoftware and circuit diagram are basically opened, and application reports will be invited.
|