Hiromitsu Furukawa (Senior Researcher) of the Optical Sensing Group, the Electronics and Photonics Research Institute (Director: Satoshi Haraichi), the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST; President: Ryoji Chubachi), has developed a prototype spectrometer which provides non-invasive testing of substances in blood by means of gathering weak body-penetrating light effectively.
The main features of the spectrometer are highly sensitive, high-speed measurement of near-infrared light, and portability. These achieve the continuous measurement of the weak transmitted light through the body to monitor the blood fat level in real time instead of the conventional testing with blood taking. The spectrometer can be used for daily management of caloric intake at home or work, and could therefore contribute to preventing the metabolic syndrome etc. Additional development of non-invasive monitoring of substances linked to various diseases is expected in the future.
The details of this technology will be presented at InterOpto 2014 to be held on October 15-17, 2014, at Pacifico Yokohama (Yokohama, Kanagawa).
 |
|
Prototype spectrometer for non-invasive measurement of substances in blood |
Blood monitoring devices that can be used easily at home or work have recently been attracting a great deal of attention from a preventive medicine perspective. For example, if caloric intake or a barometer of health could be extracted from these devices, it would be useful for the management of health risk and dietary habits in order to prevent lifestyle-related diseases like diabetes, arteriosclerosis, hyperlipidemia, which can cause myocardial infarction and brain infarction. Fat intake is drawing attention recently, as seen in the growing popularity of “Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU)” that suppress fat absorption as more people worry about lifestyle-related diseases. However, it takes a long time for the nutrients of meals to be reflected in changes in weight or body fat. Therefore, a major issue is the fact that management of the quality of daily meals cannot be performed with only the current weight and body fat scales.
AIST has been conducting research and development of non-invasive biological measurements. With “Research and Development Project for a High-Precision Retinal Imaging Device” of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization from 2005 to 2010, AIST developed early diagnosis technology for diabetic retinopathy and malignant hypertension, which can be detected through an optically transparent “eye”, and manufactured a practical prototype.
Because diabetes and the metabolic syndrome are rapidly increasing with economic growth and Westernization of diets in Japan, AIST is also aiming to develop technologies that can contribute to preventive medicine, such as blood-testing technology to measure the weak transmitted light through the opaque human body with light intensity below the safety threshold. In the present study, AIST developed a spectrometer with the highest sensitivity in the world. AIST completed a compact and portable prototype that can perform rapid and stable measurements.
The diffuse reflection method is the mainstream approach to obtain internal signal of the body using light because light is attenuated immediately after entering the body. Certainly the body-penetrating light would provide a wealth of information about the inside of the body, current spectrometers require longer measurement times (exposure) for the weak signal, which causes problems such as difficulty in properly obtaining signals when the body moves during the measurement or in keeping up with dynamic changes. More intense light cannot be employed to improve the signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio, because there is a limit to the light intensity that can be used to irradiate the body from a safety standpoint.
In this study, these issues were thus resolved by collecting light from a large area so that even weak light can be measured rapidly. As a result, sensitivity over 1,000 times higher than that of current spectrometers was achieved, which enabled real-time spectroscopy of body-penetrating light while the incident light intensity is maintained within a safe range. In the developed prototype spectrometer, Fourier-transform spectroscopy was adopted as the base, which does not restrict the area of the light source. Furthermore, some inventions for enhancing the sensitivity, including effective guiding of the penetrating light from the bulky body to the device and effective use of polarization properties, were added.
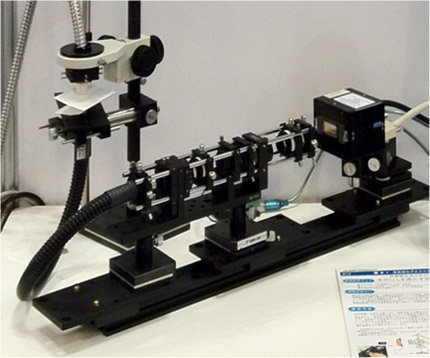
Figure 1(a) shows a prototype that AIST designed and manufactured in the initial stage of this R&D, whereas Fig. 1(b) shows the latest prototype device. In addition to improved safety and operability, the device was also made more transportable by reducing the size and weight.
|
(a) |
 |
|
(b) |
 |
Figure 1 : Prototype devices for non-invasive blood testing using high-sensitivity spectroscopy
(a) A prototype high-sensitivity spectrometer developed in the initial stage
(b) The latest prototype device with increased stability and portability
Blood fat are measured by placing a fingertip on the opening of the optical fiber. |
Figure 2 shows time-dependence of the light intensity at the wavelength corresponding to blood lipids measured by the developed spectrometer. It demonstrates that the signal from lipids show regular and periodic variation. Because blood vessels repeatedly constrict and dilate with pulsations, substances within the blood can be detected by extracting only the signal with periodic changes from the measured spectra.
Based on measurements by the developed spectrometer, lipid components in blood before and after a meal were estimated. The analysis showed that triglycerides increased after the meal and reached a peak approximately 4 hours later (Fig. 3).
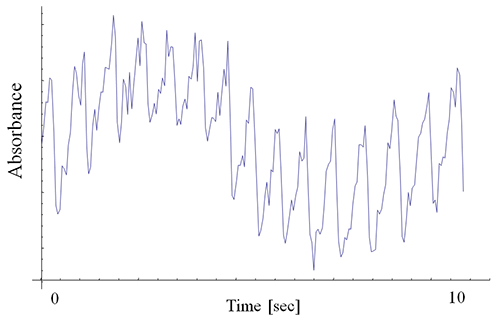 |
Figure 2 : An example of changes in spectral intensity caused by pulsations
Each cycle indicates a change in absorbance caused by a pulsation (approximately 14 cycles in 10 seconds). |
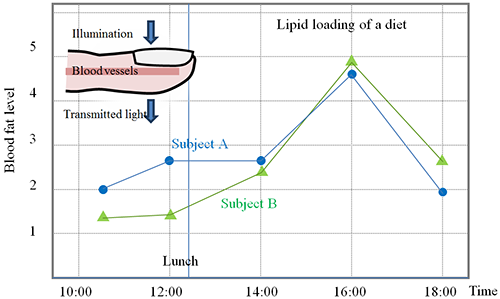 |
Figure 3 : Blood fat level obtained by measuring a fingertip using the developed spectrometer
Triglycerides in blood increase after lunch and then decrease. |
The company collaborating with AIST in this R&D aims to release this high-sensitivity spectrometer to market in the next fiscal year. AIST plans to improve the device and the algorithms for spectroscopic analysis to perform non-invasive and real-time measurements of various substances in blood such as blood glucose.