Update(MM/DD/YYYY):12/02/2005
Providing Computing Power on demand Using the Grid technologies
- The start of the proof-of-concept experiment on GridASP utility computing business -
Key points
-
GridASP is a new business model that uses grid technology to provide many different types of computing environments to meet user demands.
-
The β version of GridASP Toolkit, the softwareen embodying ASP business model, has been completed, and is publicly released as free software.
-
This software provides combinations of different providers' CPUs and applications to meet users' needs.
-
The proof-of-concept experiments with several private companies using GridASP Toolkit has begun in November.
Synopsis
As one of business diversification using grid technology, the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST, President: Hiroyuki Yoshikawa) presents new business model "GridASPTM*" which provides the required amount of computing power at the right time as a utility for businesses, research organizations, and other users.
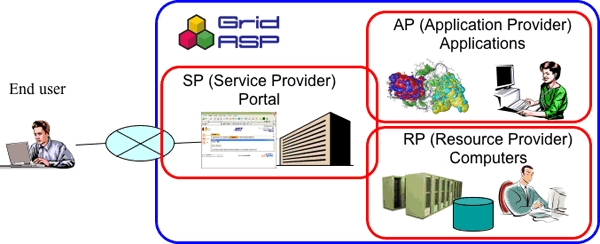
In the existing ASP (Application Service Provider) model, there are high overhead costs associated with preparing computers and operators for each application, so it is expensive for the user. However, as we can see in Figure 1, GridASP divides companies into three providers that can respectively provide applications, computers, and portals which can be supplied in any combination to meet user demands. This can raise the operating efficiency of each company and reduce the costs to the user.
The AIST has been developing software called GridASP Toolkit that can embody the framework of GridASP. The β version has been completed, which is being publicly released as free software. Part of this software was developed as METI's Business Grid Computing Project that was launched in 2003.
In addition, a test environment was created in which proof-of-concept experiment were begun using GridASP Toolkit in cooperation with companies to provide services. These experiments will be conducted to not only examine the functionality of the software, but also to identify problems associated with business applications, to estimate service price, and to investigate application license style, among other things.
 |
|
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of GridASP
|
* GridASP is a registered trademark of the AIST in Japan.
Background
ASP has already been used to run applications on external computers, but in those cases a special portal and computer were prepared so that one organization could run special applications. As a result, there were several problems, including
-
Business could not be started until the portal, computer(s), applications, and all resources and environments had been prepared.
-
Computers were idle when there were no requests from users.
-
Business opportunities were lost when there were more requests than the system could handle.
-
An operator was needed, even for small computer systems, and the operator's fees added to the user's costs.
-
While the system was supposed to prevent product data from many user companies from being disclosed to outsiders, the ASP companies did know who was using what data.
Given that and other problems, ASP has not always appropriate choice for companies, research organizations, etc., to use to provide their required computing power.
Solutions using GridASP
GridASP is composed of suitable combinations of calculation resources that have been pooled together in a grid environment, to build a virtual computer system which provides the required amount of computing power at the right time to users. We assume applications which need computing power at companies, research organizations, etc. rapidly develop business models of utility computing, and thus target the services that execute these applications. For example, candidates include design and analysis work in the automobile and semiconductor, risk analysis in the financial industry, and so on.
In GridASP, conventional ASP is divided into 3 providers, that is, a Service Provider (SP) who manages the portal; an Application Provider (AP), who provides the applications; and a Resource Provider (RP) who provides the computers. Connecting these 3 providers may have the following advantages over conventional ASP:
-
Using just the special skills, or the existing resources of the providers, it may be possible to participate in this business.
-
The use of specialized skills can improve the ROI (Return of investment). For example, if clusters are managed well, the operating costs per computer in a large-scale operation can be brought down below the level of other companies.
-
By contracting with multiple portal service providers, resource providers can take orders from other portals, even when there are few requests from a portal. This can make more efficient use of computer resources.
-
By contracting with multiple resource providers, portal service providers can use other resource providers when the computer of one resource provider is full. The portal service provider does not loose business opportunity.
-
Portal service providers can select the applications tailored to end users (such as structural analysis, fluid analysis, etc. in the automobile industry) from among the applications prepared by multiple application providers. This can add value to the portal for the end user.
-
While portal service providers must be able to recognize the end user, the resource provider does not. On the other hand, the resource provider needs to know what sorts of data are being made, while the portal service provider does not need to know the specifics of the analytical data. By this way, there is no company to know both "who" and "what."
-
After the application has been executed on the computer of the resource provider and the results returned to the portal service provider, all related files are deleted, preventing leaks of user data from being made to third parties.
GridASP Toolkit
We are developing the GridASP Toolkit, which is used for linkages between multiple providers to provide services for executing applications. Part of this software was developed as METI's Business Grid Computing Project.
This software features the following functions: virtualizing computers so that the program can be run on any computer; allowing automatic deployment of applications from a remote computer; providing anonymity in calculations so that resource provider will not know who is doing what calculations; and a broker function which selects a suitable computer to carry out a request from an end user to execute an application. The just-completed b version of this software has been publicly released under provision of the Apache Software License. It should be noted that when using GridASP Toolkit to construct a system, it is necessary to use other kinds of software such as Globus Toolkit 4.
The proof-of-concept experiments for GridASP
The proof-of-concept experiments are conducted to verify the feasibility of GridASP for business uses. These experiments are divided into two parts:
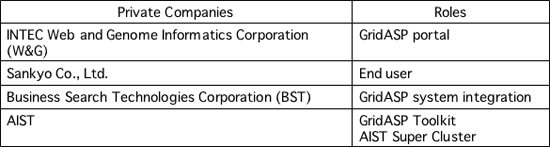
The first part involves verifying the functions of the newly-developed GridASP Toolkit software, which is done as part of METI's Business Grid Computing Project. For a list of participating companies, please refer to the list below. Using chemistry applications required by pharmaceutical companies, the computer utilizes part of the super cluster at the AIST. The system has already been constructed, and is now in a 3-month trial period which started in October. These experiments will provide a venue for evaluating the system construction, operation, and utilization of GridASP Toolkit from the standpoints of different players.
|
Table 1 Companies involved in the first joint proof-of-concept experiment for GridASP (in Japanese alphabetical order) |
 |
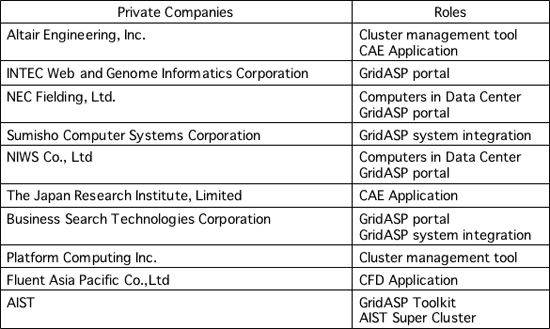
The second part will focus on the feasibility of using the system in the business. As an original activity of AIST, joint research will be conducted with a variety of companies. The main differences with the first part are as follows:
-
Computers are provided by the companies those are operating the commercial data center
-
Applications are provided from commercial application vendors
-
Numerous companies are involved
This part of the experiments will be used to identify issues with using GridASP for business purposes, making a rough estimate of service price for end users, and investigating new application license styles. Preparations for these experiments were began with participating in August; the operation of the trial system has begun in November.
|
Table 2 Companies involved in the second proof-of-concept experiment for GridASP (in Japanese alphabetical order) |
 |
Future Prospects
In order to apply GridASP to business uses, it is necessary not only to promote its use through the public release of the GridASP Toolkit software, but also to take an organic approach to the matter through software support, management of certificate authority and certifying enterprises, etc. To achieve this objective, plans are being made to establish the GridASP consortium (tentative name) that can help promote GridASP business.